RTX 5080 Power Requirements: Do You Need a New Cable? (2026 Update)
Quick Summary of the RTX 5080 Power Specs
These are the minimum requirements for the RTX 5080:
- Total Graphics Power (TGP): 360W (Stock)
- Recommended PSU: 850W (Minimum) | 1000W (Recommended for headroom)
- Power Connector: 12V-2×6 (Native PCIe 5.1)
- Safe for Old PSUs? Yes, but only with a high-quality 3-way 8-pin adapter or a native ATX 3.1 cable.
The 12V-2×6 Standard: Is the “Melting” Risk Over?

The biggest concern for gamers since the previous generation has been the 16-pin connector. The RTX 5080 utilizes the 12V-2×6 standard, which is the refined version of the original 12VHPWR connector.
According to the PCI-SIG specifications, the 12V-2×6 header features shorter sense pins. This ensures that the GPU won’t pull full power unless the cable is completely seated.
Pro Tip: Just as a monitor stuck at 60Hz is often caused by a poorly seated HDMI cable, a “melting” GPU is almost always caused by a 16-pin cable that isn’t clicked in all the way. With the RTX 5080, the hardware is much safer, but the “click” is still necessary.
Can Your Current PSU Handle the RTX 5080?
Scenario A: You have an ATX 3.0/3.1 PSU
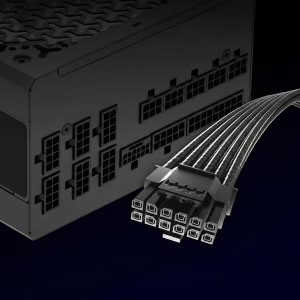
You are good to go. Your power supply likely came with a native 16-pin cable. You get the benefit of a single, clean cable run and better transient spike management.
Scenario B: You have an older ATX 2.0 PSU (8-pin slots)
You can still run an RTX 5080, but you will need an adapter. Most 5080s ship with a “3-into-1” adapter (3x 8-pin PCIe cables into one 16-pin connector).
Warning: Do not daisy-chain your 8-pin cables. Each of the three connectors on the adapter should have its own dedicated cable leading back to the PSU.
Wattage Requirements: 850W vs 1000W
While the RTX 5080 is rated for 360W, modern CPUs (like the i9-14900K or the newer Ryzen 9000 series) can draw massive amounts of power during gaming.
| Component | Estimated Power Draw |
| RTX 5080 (Gaming) | 360W |
| High-End CPU | 150W – 250W |
| Motherboard/Fans/RGB | 50W |
| Total System Draw | ~660W |
Why 850W is the “Bare Minimum”: For system stability and preserving your hardware, you never want your PSU to run at 90% capacity. Some problems you might encounter when your total system draw is close to your power supply capacity:
- Transient Spikes: GPUs don’t pull power in a straight line. Instead, they have bursts where they can draw double their rated power for milliseconds. If your PSU is already at 90%, these spikes can trigger the Over Current Protection (OCP), causing your PC to instantly shut down in the middle of a game.
- The Efficiency Trade-off: Most power supplies are efficient when running at 50% to 60% load. When the PSU is running at 90%+, it generates significantly more heat, forcing the internal fans to spin at max RPM.
- Component Degradation: Power supplies use capacitors to “smooth out” electricity. When you run your PSU near its maximum capacity 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, it creates internal heat that dries out these capacitors over time. This shortens the lifespan of the Power Supply Unit and puts your expensive GPU at risk if the voltage ripple becomes unstable.
What happens if your PSU is too weak?
If you face any of the following issues, then it’s likely that your build is underpowered:
- Hard Crashes to Desktop (CTD): Your game closes without an error message because the GPU didn’t get the voltage it needed during an intense scene.
- Blue Screens of Death (BSOD): System-wide instability caused by fluctuating power to the motherboard and RAM.
- The “Click of Death”: A click followed by a black screen. This is your PSU’s safety relay tripping to prevent a fire because it couldn’t handle the load.
An 850W unit gives you roughly 20% breathing room, which is the “sweet spot” for efficiency and noise. If you plan to overclock, we strongly recommend a 1000W unit. A 1000W unit ensures that even during the most intense 4K gaming sessions, your PSU is sitting comfortably at 65% load, staying cool and quiet.
Top 3 Recommended PSUs for RTX 5080
Best Overall: Corsair RM1000x (2024 Version)
The Corsair RM1000x (2024 version) is the 1000W standard for high-end builds. Fully ATX 3.1 and PCIe 5.1 compliant, the RM1000x offers stability and silence. For an RTX 5080 build, the 1000W capacity ensures you stay in the efficiency “sweet spot” while leaving room for future upgrades.
The 2024 version includes color-coded connectors on the cable head, making it much easier to confirm that your power cable is fully seated. There’s no need for adapters with its native 12V-2×6 cable.
Best Value: MSI MAG A850GL PCIE5
The MSI MAG A850GL is a really good choice, offering top-tier protection at a mid-range price. Its surprisingly light weight compared to older EVGA units makes it easier to handle during installation. This PSU is ideal for standard mid-tower cases where you want a power solution that can fit both last-gen and current-gen hardware.
PC Builders have noted the professional packaging, with all modular cables secured in a dedicated Velcro pouch and the unit protected by high-quality foam to prevent shipping damage.
It runs incredibly quiet with very little coil whine. If you’ve had good experiences with MSI motherboards, then you should expect this PSU to match your expectations.
Best SFX (Small Form Factor): Corsair SF1000 (Platinum)

Finding an SFX-L power supply that delivers 1000 watts for an affordable price is a challenge. That’s one of the reasons why the SF1000 is a category leader. It is powerful enough to handle overclocked 40-series and 50-series cards, as well as power-hungry AMD chips like the 7900 XTX.
It features ultra-flexible, non-braided wires. The lack of added bulk from braiding is a massive advantage in tight ITX builds, making cable routing significantly easier.
The fan is so quiet that you wouldn’t notice it under moderate loads. Plus, it provides enough modular PCIe connectors to use a dedicated cable for every single port on your GPU, ensuring stable power delivery.
Important Compatibility Note: Some users have reported grounding issues when pairing this PSU with the Phanteks Shift XT case, resulting in static shocks. However, it performs flawlessly in other popular small cases like the Lian Li A4-H2O.
Comparison Summary Table
| Feature | MSI MAG A850GL | Corsair RM1000x | Corsair SF1000 |
| Form Factor | ATX (Standard) | ATX (Standard) | SFX-L (Compact) |
| Max Wattage | 850W | 1000W | 1000W |
| Best For | Budget-Conscious | High-End Performance | Small Form Factor (ITX) |
| Unique Perk | Very Lightweight | Color-Coded Cables | Ultra-Flexible Wires |
| Price Tier | $ | $$ | $$$ |
The 2026 Build Checklist
- Power: Is your 12V-2×6 cable clicked in until it sounds?
- Display: Are you using a certified HDMI 2.1 cable for your 240Hz monitor?
- Network: Don’t let high ping ruin your high FPS. If you’ve upgraded to a Wi-Fi 7 router, ensure you are using a Cat6a Ethernet cable to feed it.










This was beautiful Admin. Thank you for your reflections.
Most welcome… I hope it was helpful when buying a new power cable for your GPU.
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
Thanks for stopping to read. If you don’t mind, how did you find the site?